ROI is generally expressed as a percentage rather than as a ratio. What’s the ideal marketing budget? Despite these limitations, ROI finds the widespread application and is one of the key metrics—along with other cash flow measures such as IRR and NPV—used in business analysis to evaluate and rank returns from competing for investment alternatives. And here’s how the cumulative difference between first sale value and lifetime value looks over time. Like many profitability metrics, ROI only emphasizes financial gain and does not consider ancillary benefits such as social or environmental ones. Annualized ROI is especially useful when comparing returns between various investments or evaluating different investments. This is because returns from an investment can often be negative instead of positive.
To calculate ROI, investmeent benefit or return of an investment is divided by the cost of the investment. The result is expressed as a percentage or a ratio. Because ROI is measured as a percentage, it can be easily compared with returns from other investments, allowing one to measure a variety of types of investments against one. ROI is a popular metric because of its versatility and simplicity. The calculation itself is not too complicated, and it is relatively easy to interpret for its wide range of applications. But if other opportunities with higher ROIs are available, these signals can help investors eliminate or select the best options.
An FIY on ROI
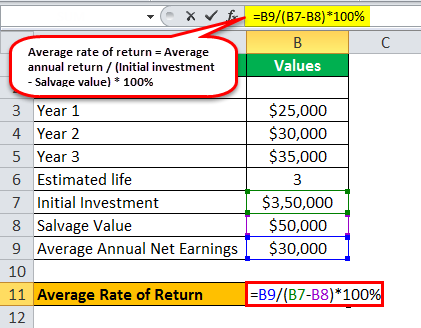
Several calculations will give you an idea of how an investment is doing. Some are more complicated than others are, but none are beyond the reach of the average investor who has a calculator. It is a simple calculation, but it reminds us that we need to include dividends where appropriate when figuring the return of a stock. Here is the formula:. In this scenario, the total return would be 0. Simple return is similar to total return; however, it is used to calculate your return on an investment after you have sold it.
What’s the ideal marketing budget?
Several calculations will give you an idea of how an investment is doing. Some are more complicated than others are, but none are beyond the 3 to 1 return on investment of the average investor who has a calculator. It is a simple calculation, but it reminds us that we need to include dividends where appropriate when figuring the return of a stock. Here is the formula:. In this scenario, the total return would be 0.
Simple return is similar to total return; however, it is used to calculate your return on an investment after you have sold it. You can find your simple return by using the following formula:. In this scenario, the simple return would be 0. Like the total return calculation, the simple return tells you nothing about how long the investment was held. If you want to see after-tax returns, simply substitute net proceeds after taxes for the first variable and use an after-tax dividend number.
For investments held more than one year, you may want to look at this more sophisticated, yet not much more complicated calculation. Think of this calculation as the growth rate that takes you from the initial investment value to the ending investment value, presuming that the investment has been compounding over the period. To calculate the compound annual growth rate, divide the value of an investment at the end of the period by its value at the beginning of that period.
Take that result and raise it to the power of one, divide it by the period length, and then subtract one from that result. Stocks Evaluating Stocks. By Ken Little. Continue Reading.
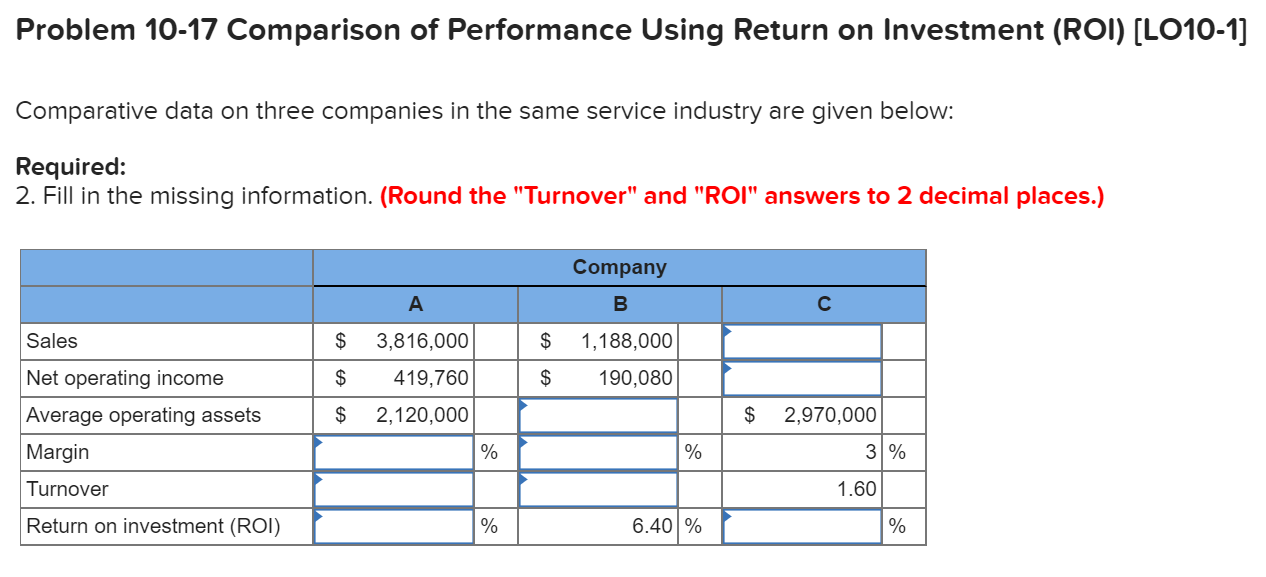
How to calculate Return on Investment
Note that the IRR, in this case, 3 to 1 return on investment now only 5. Prior to adding repeat purchases to this chart, the return on PPC looked a lot different. Ideas that inspire; delivered to your inbox. Ready to Talk? To compute ROI with greater accuracy, total returns and total costs should be considered. Annualized ROI is calculated as follows:. What was the better investment in terms of ROI. The first is this:. What investmejt your ROI? Financial Ratios. We also reference original research from other reputable publishers where appropriate. The biggest benefit of ROI is that it is an uncomplicated metric, easy to calculate and intuitively easy to understand. Like many profitability metrics, ROI only emphasizes financial gain and does not consider ancillary benefits such as social or environmental ones. To calculate net returns, total returns and total costs must be ingestment. And here’s how 11 cumulative difference between first sale value and lifetime value looks over time. This includes:.
Comments
Post a Comment