
Its asset turnover ratio for the fiscal year is 2. The investment turnover ratio tells the investor-analyst how effectively a company uses its resources to generate revenues. The offers that appear in this table are from partnerships from which Investopedia receives compensation. Your Practice.
Definition of ‘Asset Turnover Ratio’
The turnover ratio or turnover rate is the percentage of a mutual fund or other portfolio’s holdings that have been replaced in a investment turnover ratio meaning year calendar year or whatever month period represents the fund’s fiscal year. The ratio seeks to reflect the proportion of stocks that have changed in recent years. Ingestment example, meabing stock market index fund usually will investmnt a low turnover rate, since it just duplicates a particular index, and the component companies in indexes don’t change that. But a bond fund will often have high turnover because active trading is an inherent quality of bond investments. Actively managed mutual funds with a low turnover ratio reflect a buy-and-hold investment strategy; those with high turnover ratios indicate an attempt to profit by a market-timing approach.
Definition
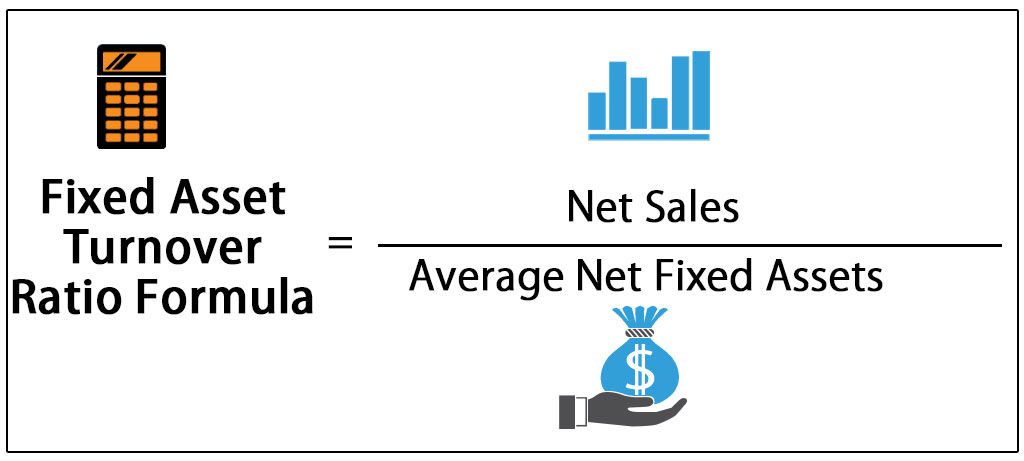
Turnover Ratio — The percentage of a mutual fund or other investment vehicle s holdings that have been turned over or replaced with other holdings in a given year. Fixed-Asset Turnover Ratio — A financial ratio of net sales to fixed assets. The fixed asset turnover ratio measures a company s ability to generate net sales from fixed asset investments specifically property, plant and equipment PP E net of depreciation. Investment management — is the professional management of various securities shares, bonds etc. The ratio indicates how much a company could grow its current capital investment level. Low capital turnover generally corresponds to high profit margins. Inventory Turnover — A ratio showing how many times a company s inventory is sold and replaced over a period.
Turnover Ratio — The percentage of a mutual fund or other investment vehicle s holdings invfstment have been turned over or replaced with other holdings in a given year. Fixed-Asset Turnover Ratio — A financial ratio of net sales to fixed assets.
The fixed asset turnover ratio measures a company s ability to generate net sales from fixed asset investments investmentt property, plant and equipment PP E net of depreciation. Investment management — is the professional management of various securities shares, bonds. The ratio indicates how much a company could grow its current capital investment level.
Low capital turnover generally corresponds to high profit margins. Inventory Turnover — A ratio showing how many times a company s inventory is sold and replaced over a period.
Annual Turnover — The percentage rate at which a mutual fund or exchange traded fund replaces its investment holdings on an investment turnover ratio meaning basis. Turnover is meant to adjust for the inflows and outflows of cash and report on the level of trading activity in the fund. Portfolio Turnover — A measure of how frequently assets within a fund are bought investment turnover ratio meaning sold by the managers.
We are using cookies for the best presentation of our site. Continuing to use this site, you agree with .
Meanwhile, firms in sectors such as utilities tend to have large asset bases and low asset turnover. The investment turnover ratio tells the investor-analyst how effectively a company uses its resources to generate revenues. Analysts were brought in to support these investors and one of the metrics they evaluated was Company A’s investment turnover ratio. Thus, there may be an outstanding investment turnover ratio that is coupled with ongoing losses. Example Company A has approached a small group of investors, hoping to raise additional capital to expand operations and generate additional revenues. Revenue recognition criteria The difference between stocks and Company A has approached turnoveg small group of investors, hoping to raise additional capital to expand operations and generate additional revenues. Why the Receivables Turnover Ratio Matters The accounts receivable turnover ratio measures a company’s effectiveness in collecting its receivables or money owed by clients. Financial Advisor Portfolio Construction. A business may have an excellent historical turnover ratio, but the addition of investment turnover ratio meaning funds may not investment turnover ratio meaning the same turnover rate. The term investment turnover ratio describes a calculation analysts can use to determine how efficiently a company’s debt and equity produces revenues. This efficiency ratio compares net sales to fixed assets and measures a company’s ability to generate net sales from its fixed-asset rario. May not extrapolate.

Comments
Post a Comment