Interest Rates. The interest is less compared with the previous case, as a result of the lower compounding frequency. Instead of calculating interest on a finite number of periods, such as yearly or monthly, continuous compounding calculates interest assuming constant compounding over an infinite number of periods.
While this is not possible in practice, the concept of continuously compounded interest is important in finance. It is an extreme case of compoundingas most interest is compounded on a monthly, quarterly or semiannual basis. In theory, continuously compounded interest means that an account balance is constantly earning interest, as well as refeeding that interest back into the balance so that it, too, earns. Instead of calculating interest on a finite number of periods, such as yearly or monthly, continuous compounding calculates interest assuming constant compounding over an infinite number of periods. Even with very large investment amounts, the difference in the total interest earned through continuous compounding is not very high when compared to traditional compounding periods.

Continuous-repayment mortgage — Analogous to continuous compounding, a continuous annuity[1][2] is an ordinary annuity in which the payment interval is narrowed indefinitely. Convenience yield — A convenience yield is an adjustment to the cost of carry in the non arbitrage pricing formula for forward prices in markets with trading constraints. Let Ft,T be the forward price of an asset with initial price St and maturity T. Rate of return — In finance, rate of return ROR , also known as return on investment ROI , rate of profit or sometimes just return, is the ratio of money gained or lost whether realized or unrealized on an investment relative to the amount of money invested. Time value of money — The time value of money is the value of money figuring in a given amount of interest earned over a given amount of time. The time value of money is the central concept in finance theory.
While this continuously compounded interest rate investment not possible in practice, the concept of continuously compounded interest is important in finance. It is an extreme case of compoundingas most interest is compounded on a monthly, quarterly or semiannual basis. In theory, continuously compounded interest means that an account balance is constantly earning interest, as well as refeeding that interest back jnterest the balance so that it, too, earns.
Instead of calculating comoounded on a finite number of periods, such as yearly or monthly, continuous compounding calculates interest assuming constant compounding over an infinite number of periods. Even with very large investment amounts, the difference in the total interest earned through continuous compounding is not very high when compared to traditional compounding periods.
The formula for continuous compounding is derived from the formula for the future value of an interest-bearing investment:. The following examples show the ending value of the investment when the interest is compounded annually, semiannually, quarterly, monthly, daily and continuously.
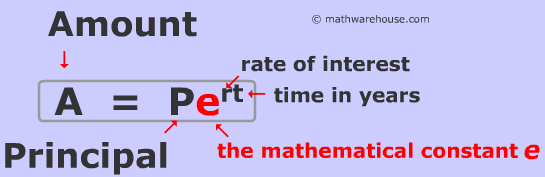
Interest Rates. Investing Essentials. Fixed Income Essentials. Your Money. Personal Finance. Your Practice. Popular Courses. Login Newsletters. Stocks Dividend Stocks. What is Continuous Compounding? The formula for compound interest over finite periods of time takes into account four variables:.
Key Takeaways Most interest is compounded on a semi-annually, quarterly or monthly basis. Continuously compounded interest assumes continuously compounded interest rate investment interest is compounded and added back into an initial value an infinite number of times. Compare Investment Accounts. The offers that appear in this table are from partnerships from which Investopedia receives compensation.
Related Terms Learn About Compounding Compounding is the process in which an asset’s earnings, from either capital gains or interest, are reinvested to generate additional earnings over time. Time Value of Money TVM Definition The time value of money compoumded the idea that money rqte available is worth more than the same amount in the future due to its potential earning capacity.
Compound Interest Definition Compound interest is the numerical value that is calculated on the initial principal and the accumulated interest of previous periods of a deposit or loan.
Compound interest is common on loans but is less often used with deposit accounts. What Is Cumulative Interest? Cumulative interest is the sum of all interest payments made on a loan over a inevstment time period. What the Effective Annual Interest Rate Tells Us The effective annual coninuously rate is the interest rate that is actually earned or paid on an investment, loan or other financial product due to the ingestment of compounding over a given time period.
That is, it’s calculated under the assumption that any interest paid is included in the principal payments balance. Partner Links. Related Articles. Compoknded Essentials How do I use the ratw of 72 to calculate continuous compounding? Interest Rates Continuous Compound Interest.
Compound Interest — Easy Example + Practice
James and John Knapton, et al. Hidden categories: Wikipedia articles incorporating a citation from the Cyclopaedia Wikipedia articles incorporating text from Cyclopaedia Wikipedia articles incorporating a citation from the Cyclopaedia without an article title parameter Articles with short description Wikipedia articles needing clarification from July Articles needing additional references from Continuously compounded interest rate investment All articles needing additional references Wikipedia articles with GND identifiers Wikipedia articles with LCCN identifiers. Your Money. Related Terms Forward Price Definition The predetermined delivery price of a forward contract, as agreed on and calculated by the buyer and seller. A formula that is accurate to continuously compounded interest rate investment a few percent can be found by noting that for typical U. For any continuously differentiable accumulation function a lnterestthe force of interest, or more generally the logarithmic or continuously compounded return is a function of time defined as follows:. The interest on loans and mortgages that are amortized—that is, have a contihuously monthly payment until the loan has been paid off—is often compounded monthly. See also: Logarithmic return. Both the nominal interest rate and the compounding frequency are required in order to compare interest-bearing financial instruments. What’s so great about the continuously compounded rate or return that we will denote with r c? What the Effective Annual Interest Rate Tells Us The effective annual interest rate is the interest rate that is actually earned or paid on an investment, loan or other financial product due to the result of compounding over a given time period. While this may not be practical, the continuously compounded interest rate offers marvelously convenient properties. Compound interest was once regarded as the worst kind of usury and was severely condemned by Roman law and the common laws of many other countries. Compounder logarithm Exponential function. John Napier Leonhard Euler. Popular Courses.
Comments
Post a Comment