
Please explain calculation of impairment test separately if any there and circumstances if any. New depreciation will be 1. If the calculated costs of holding the asset exceed the calculated fair market value, the asset is considered to be impaired.
This article discusses and shows both ways of measuring goodwill following the acquisition of a subsidiary, and how each measurement of goodwill is subject to an impairment review. This method can be referred to as the proportionate method. It determines only the goodwill that is attributable to the parent company. Another method of measuring goodwill on the acquisition of the subsidiary is to compare the fair value of the whole of the subsidiary as represented by the fair value of the consideration given by the parent and impairmrnt fair value of the non controlling interest with all of the fair value of the net assets of the subsidiary acquired. This method can be referred to as the gross or full goodwill method. Back to top. In these examples, goodwill is said to be a premium arising on acquisition.
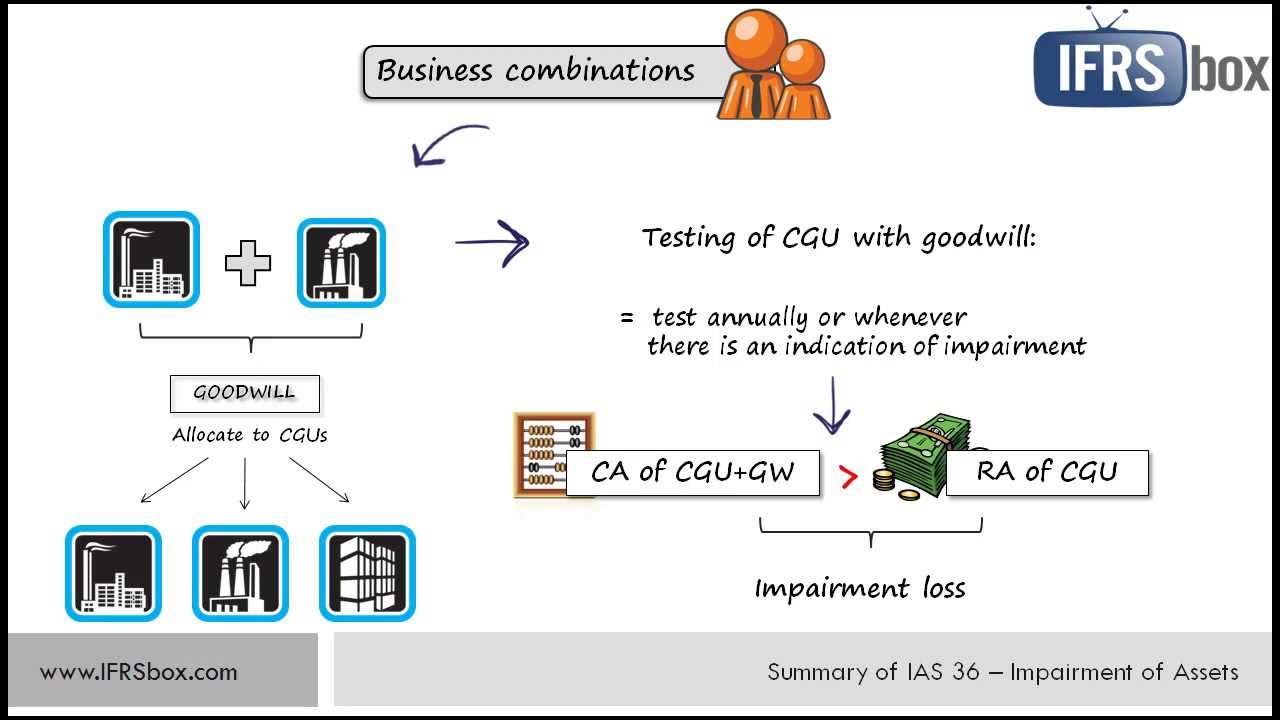
History of IAS 36
Impairment occurs when a business asset suffers a depreciation in fair market value in excess of the book value of the asset on the company’s financial statements. Under the U. The technical definition of impairment loss is a decrease in net carrying value , the acquisition cost minus depreciation, of an asset that is greater than the future undisclosed cash flow of the same asset. An impairment occurs when assets are sold or abandoned because the company no longer expects them to benefit long-run operations. This is different from a write-down , though impairment losses often result in a tax deferral for the asset. Depending on the type of asset being impaired, stockholders of a publicly held company may also lose equity in their shares, which results in a lower debt-to-equity ratio. The first step is to identify the factors that lead to the asset’s impairment.
What is an impairment of assets?
Impairment occurs when a business asset suffers a depreciation in fair market value in excess of the book value of the asset on the company’s financial statements. Under the U. The technical definition of impairment loss is a decrease in net carrying valuethe acquisition cost minus depreciation, of an asset that is greater than the future undisclosed cash flow of the same asset.
An impairment occurs when assets are sold or abandoned because the company no longer expects them to benefit long-run operations. This is different from a write-downthough impairment losses often result in a tax deferral for the asset.
Depending on the type of asset being impaired, stockholders of a publicly held company may also lose equity in their shares, which results in a lower debt-to-equity ratio.
The first step is to identify the factors that lead to the asset’s impairment. Some factors may include changes in market conditions, new legislation or regulatory enforcement, turnover in the workforce or impairment loss of investment in subsidiary asset functionality due to aging. In some circumstances, the asset itself may be functioning as well as ever, but new technology or new techniques may cause the fair market value of the asset to drop significantly.
A fair market calculation is key; asset impairment cannot be recognized without a good approximation of fair market value. Fair market value is the price the asset would fetch if it was sold on the market. This is sometimes described as the future cash flow the asset would expect to generate in continued business operations.
Another term for this value is «recoverable. Carrying value does not need to be recalculated at this time since it exists in previous accounting records. If the calculated costs of holding the asset exceed the calculated fair market value, the asset is considered to be impaired. If the asset in question is going to be disposed of, the costs associated with the disposal must be added back into the net of the future net value less the carrying value.
Impairment losses are either recognized through the cost model or the revaluation model, depending on whether the debited amount was changed through the new, adjusted fair market valuation described. Even when impairment results in a small tax benefit for the company, the realization of impairment is bad for the company as a.
It usually represents the need for an increased reinvestment. Financial Analysis. Your Money. Personal Finance. Your Practice. Popular Courses. Login Newsletters. Compare Investment Accounts. The offers that appear in this table are from partnerships from which Investopedia receives compensation. Related Articles. Accounting How do you write off impaired assets from the financial statement?
Accounting Amortization vs. Impairment of Tangible Assets: What’s the Difference? Partner Links. Impairment Definition Impairment describes a permanent reduction in the value of a company’s asset, such as a fixed asset or intangible, to below its carrying value.
What Is a Capital Asset? A capital asset is an asset with a useful life longer than a year that is not intended for sale in the regular course of the business’s operation. Defining Physical Assets A physical asset is an item of economic, commercial, or exchange value that has a tangible or material existence. Impaired Asset An impaired asset is a company’s asset that is worth less on the market than the value listed on the company’s balance sheet.
Goodwill Impairment Definition Goodwill impairment is an accounting charge that companies record when goodwill’s carrying value on financial statements exceeds its fair value.
However, some of this capex was committed initially at the time at a time before building was constructed but the work was never completed when the building was handed over to tenants. Navigation Standards. I am im;airment for insight in relation to impairment of construction in progress. Dear Sylvia May I please ask one other question in addition to the one. At the end of each reporting period, an entity is required to assess whether there is any indication that an asset may be impaired i. By far the best teaching site for accounting.
Comments
Post a Comment