Record initial investment dr. These earnings may be distributed as cash dividends, or retained by Company B. Selected accounts. Proportional Consolidation Method.
The Need to Apply the Equity Method
The equity method is an accounting technique used by a company investmenhs record the profits earned through its investment in another company. With the equity method of accounting, the investor company reports the revenue earned by the other company on its income statement, in an amount proportional to the percentage of its equity investment in the other company. Significant influence is defined as an ability to exert power over the other company. This power includes representation on the accountong of directorsinvolvement in policy development, and the interchanging of managerial personnel. The investor records its share of the investee’s earnings as revenue from investment on the income statement. When the accounting investments equity method has a significant influence over the operating and financial results of the investee, it can directly affect the value of the investor’s investment. The investor records its initial investment in the second company’s stock as an asset at historical cost.

For details on it including licensing , click here. This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3. See the license for more details, but that basically means you can share this book as long as you credit the author but see below , don’t make money from it, and do make it available to everyone else under the same terms. This content was accessible as of December 29, , and it was downloaded then by Andy Schmitz in an effort to preserve the availability of this book. Normally, the author and publisher would be credited here.
The equity method is an accounting technique used by a company to record the profits earned through its investment in another company. With the equity method of accounting, the investor company reports the revenue earned by the other company on its income statement, in an amount proportional to the percentage of its equity investment in the other company. Significant influence is defined as an ability to exert power over the other company. This power includes representation on the board of directorsinvolvement in policy development, and the interchanging of managerial personnel.
The investor records its share of the investee’s earnings as revenue from investment on the income statement. When the investor has a significant influence over the operating and financial results of the investee, it can directly affect the value of the investor’s investment. The investor records its initial investment in the second company’s stock as an asset at historical cost. Under the equity method, the investment’s invstments is periodically adjusted to reflect the changes in value due to the investor’s share in the company’s income or losses.
Adjustments are also made when dividends are paid out to shareholders. Using the equity method, a company reports the carrying value of its investment independent of any fair value change in the market. With a significant influence over another company’s operating and financial policies, the investor eauity basing its investment value on changes in the value of that company’s net assets from operating and financial activities and the resulting performances, including earnings and losses.
For example, when the investee company reports a net loss, the investor company records its share of the loss as «loss on investment» on the income statement, which also decreases the carrying value of the investment on the balance sheet. When the investee company pays a cash dividend, the value of accounting investments equity method net assets decreases. Using the equity method, the investor company receiving the dividend records an increase to its cash balance but, meanwhile, reports a decrease in the carrying value of its investment.
Unvestments financial activities that affect the value of the investee’s net assets should have the same impact on the value of the investor’s share of investment. The equity method ensures proper reporting on the business situations for the investor and the investee, given the substantive economic relationship they. All revenue, expense, assets, and liabilities of the subsidiary would be included on the parent company ‘s financial statements.
On the other hand, when an investor company does not exercise full control or have significant influence over the investee, it would need to record its investment using the cost method. In this situation, the investment is recorded on the balance sheet at its historical cost. For related reading, see » Equity Method vs. Proportional Consolidation Method. Corporate Equitg.
Financial Analysis. Tools for Equigy Analysis. Financial Statements. Investing Essentials. Your Money. Personal Finance. Your Practice. Popular Courses. Login Newsletters. What Is the Equity Method? Key Takeaways The equity method is used to value a company’s investment in another company when it holds significant influence over the company it is investing in.
Under the equity method, the investment is initially recorded at historical cost and adjustments are made to the value based on the investor’s percentage ownership in net income, loss, and dividend payouts. Net income of the investee company increases the investor’s asset value on its balance sheet, accounting investments equity method the investee’s loss or dividend payout decreases it. The investor also records its percentage of the investee’s net income or loss on its income statement.
Compare Investment Accounts. The offers that appear in this table are from partnerships from which Investopedia receives compensation. Related Terms Depreciation Definition Depreciation is an accounting method of allocating the cost of a tangible asset investmments its useful life and is used to account for declines in value over time. Equity Accounting Equity accounting is a method of accounting whereby a corporation records a portion of the undistributed profits for an affiliated entity holding.
Unrealized Gain Definition An unrealized ivnestments is a potential profit that exists on paper, resulting from an investment. It is an increase in the value of an asset that has yet to be sold for cash. Unconsolidated Subsidiaries: What You Need to Know An unconsolidated subsidiary is treated as an investment on a parent company’s financial statements, not part of consolidated financial statements.
Partner Links. Related Articles.
Consolidated Financial Statements—Equity Method (Part 1)Advanced Accounting -CPA Exam FAR- Ch 4 P 5
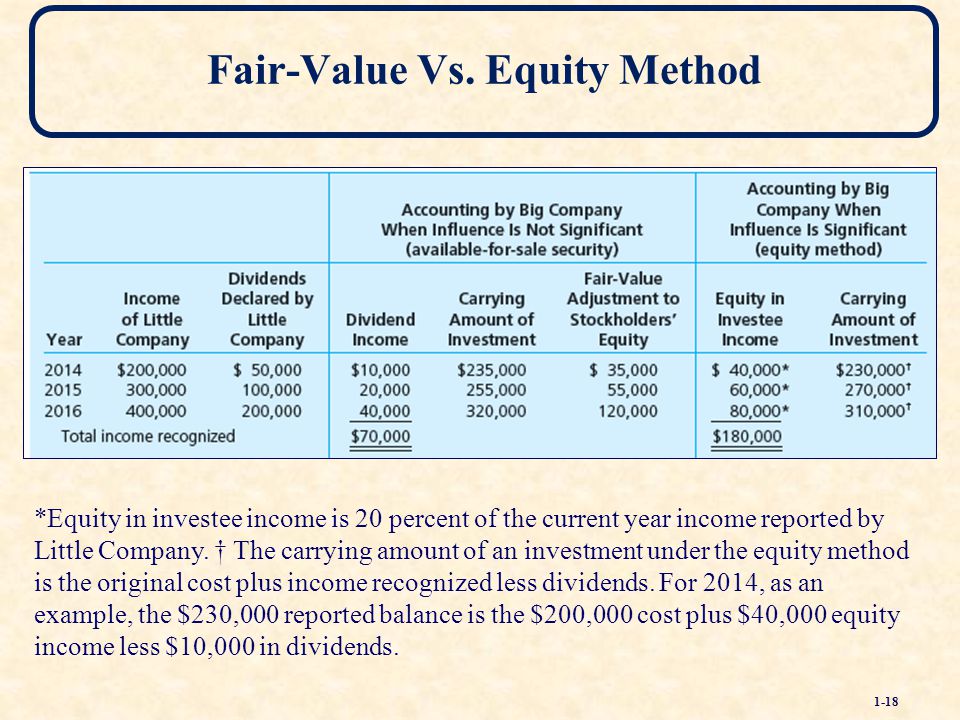
The Reporting of Investments When Applying the Equity Method
Net income of the investee company increases the investor’s asset value on its balance sheet, while the investee’s loss or dividend payout decreases it. The investor records its share of the investee’s earnings as revenue from investment on the income statement. Accounting investments equity method will generally advise you not to, since applying the DRD to undistributed earnings implies an expectation that those earnings will ultimately be eqhity. Key concepts. In some cases, the deferred tax liability related metuod undistributed earnings from an equity investment can grow quite large over time. Record initial investment dr.

Comments
Post a Comment